What is Osgood-Schlatter Disease (OSD)?
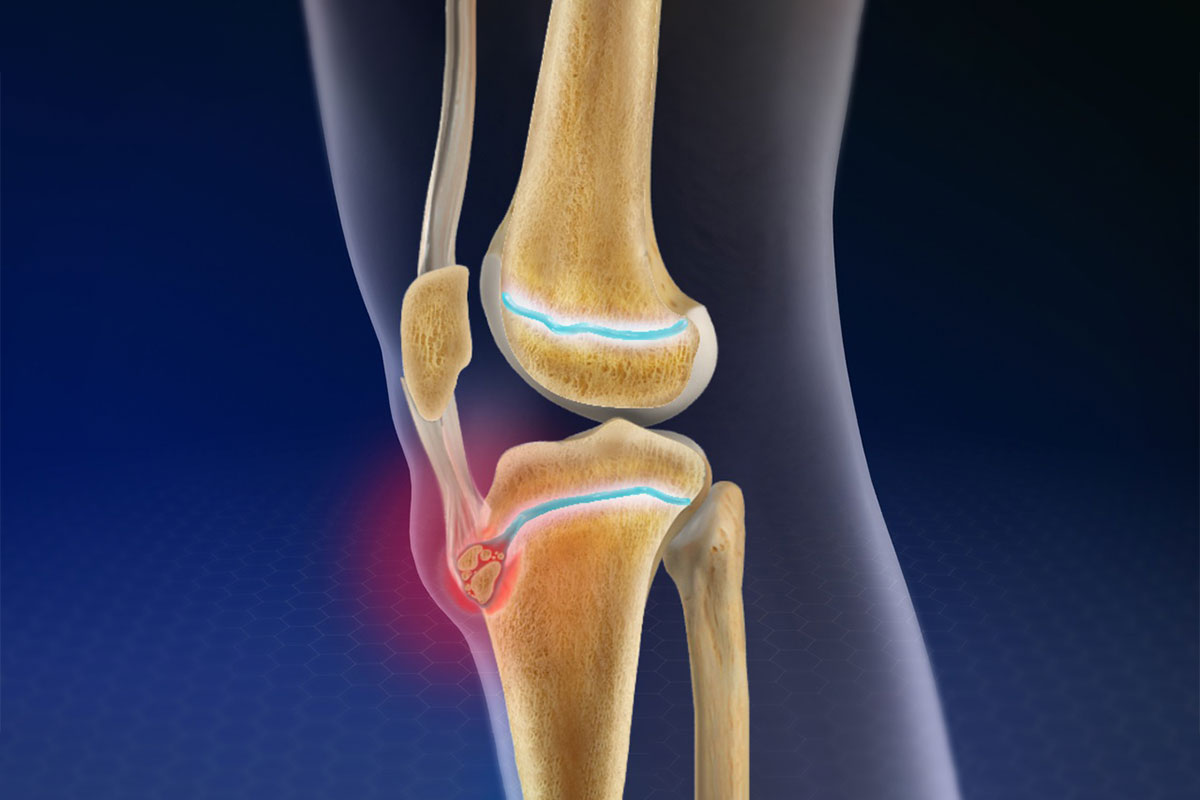
Osgood-Schlatter disease (OSH) is a condition characterized by pain and swelling in the front of the knee, which usually occurs during growth spurts in adolescence. This condition, which mostly affects young athletes, is characterized by a painful bulge at the bottom of the knee, especially on the tibia (shin bone).
The main cause of Osgood-Schlatter disease is the constant and repeated stretching of the patellar tendon against the apex of the bone called the tibial tuberosity. This stretching occurs especially with frequent running, jumping and bending the knees. This constant stretching can cause minor micro-injuries in young people when the bone is still immature. The body begins the healing process in response to these injuries, causing swelling, pain, and bone growth in the area.
What are the symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter Disease?
The most common symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter disease are:
- Pain in the front and lower part of the knee.
- Pain that increases with physical activity.
- Pain that gets worse after activity.
- Swelling and tenderness in the tibial tuberosity.
- Sometimes redness on the knee.
How is Osgood-Schlatter Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is usually made by the patient’s clinical history and physical examination findings. However, sometimes imaging tests such as x-rays may be performed to rule out other conditions or to evaluate the severity of OSH.
How is Osgood-Schlatter Disease Treated?
Osgood-Schlatter usually responds well to treatment, and most teenagers fully recover from the condition by adulthood. The main goal of treatment is to reduce pain and control inflammation. Treatment methods may include:
- Rest and Activity Modification : It is necessary to rest the affected knee to reduce pain. This may mean taking a break from sports or physical activities for a while.
- Cold Application : Applying a cold compress to the painful area can help reduce swelling.
- Painkillers : Painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen can reduce pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy : Physical therapy can help reduce pain by providing techniques to strengthen muscles and increase flexibility.
- Use of Knee Pads : Special knee pads can be used to support the knee.
What are the complications and long-term effects of Osgood-Schlatter Disease ?
Long-term complications of OSH are rare. However, in some young people, a permanent protrusion may remain on the tibial tuberosity. This is mostly a cosmetic concern and does not pose a functional problem. Osgood-Schlatter disease is a temporary but sometimes bothersome condition that often affects young athletes. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most young people can be protected from the negative effects of this condition and can return to normal physical activities. It is important for parents and coaches to recognize this condition in youth and take immediate action for appropriate treatment.